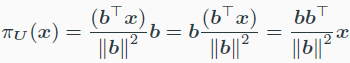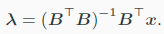(AI501) 3.linear algebra - analytic geometry
본 포스팅은 AI501 수업에서 제가 새로 알게 된 부분만 정리한 것입니다.
Norm
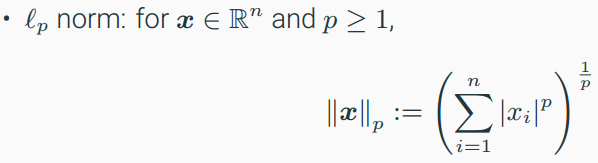
- l2 norm : 계산, 최적화 쉬움, dl에서 weight decay에 사용
- l1 norm : sparsity inducing norm, sparsifying 문제일때 사용, LASSO 알고리즘에서 사용
- $l_{\infty}$ : x1, …, xn까지 중에 가장 긴 vector
- l0 norm : norm 아님, x의 non-zero element의 개수
vector norm
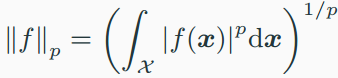
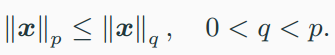
matrix norm
- Matrix의 complexity를 측정할 때, Regularizae를 통해 robust model을 만들 때 사용
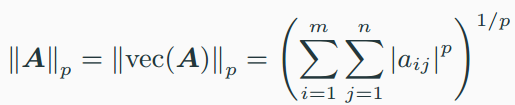
- Frobenious norm
- matrix의 l2 norm을 의미하고, optimization 문제에서 사용됨
- 특히 중요함, A의 singular value들의 제곱의 합을 의미
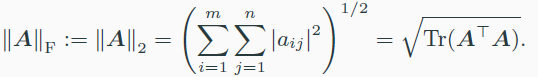
induced norm
- 벡터의 놈에서 유도된 행렬의 놈
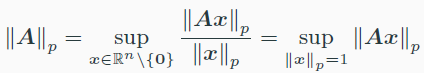
- $\lVert A\rVert_1$ 은 maximum col sum of A
- $\lVert A\rVert_\infty$ 은 maximum row sum of A
- $\lVert A\rVert_2$ 은 largest singular value of A
- Schatten norm? : matrix p-norm을 singular value로 계산하는 것?
- $\lVert A\rVert _1$ 은 nuclear norm
- $\lVert A\rVert _\infty$ 은 spectral norm
- $\lVert A\rVert _2$ 은 frobenius norm
inner product
- $\lVert x\rVert=\sqrt{<x,x>}$
- dot product는 inner product의 일종이다.
- 코시-슈파르츠
- $<x,x>^2 \leq <x,x><y,y>$
positive definite matrix
- positive definite matrix : $x^TAx\gt0$
- positive semi-definite matrix : $x^TAx\geq0$
- positive definite하면 $<x,y>=x^TAy$ 이고, $A=LL^T$로 cholesky decomposition할 수 있다. 여기서 L은 lower-triangular matrix + positive diagonal entries 이다.
Metric (distance)
- $d(x,y)=\lVert x-y\rVert=\sqrt{<x-y,x-y>}=\sqrt{(x-y)^TA(x-y)}=\sqrt{(x-y)^TLL^T(x-y)}$
- metric learning : 위 식에서 positive definite matrix A 또는 L을 를 학습하는 것
Orthogonality
- $Q^TQ=QQ^T=I$
- $\frac{<Qx,Qy>}{\lVert Qx\rVert\lVert Qy\rVert}=\frac{<x,y>}{\lVert x\rVert\lVert y\rVert}$ orthogonal matrix는 vector의 angle을 유지한다.
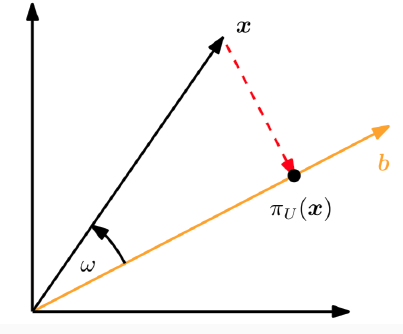
Projection
- Projection matrix P 는 idempotent($P^2=P$)이다.
- Orthogonal projection matrix : $P^2=P=P^T$
- line에 projection
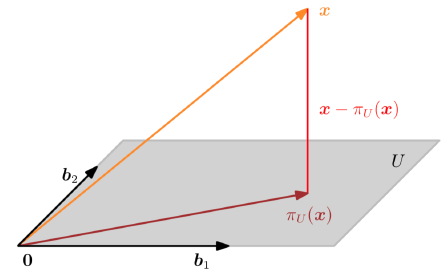
- space에 projection
- pseudo-inverse
- $(B^TB)^{-1}B^T$를 말한다.
- non-square matrix의 inverse의 일반화
- B는 full column rank이다.