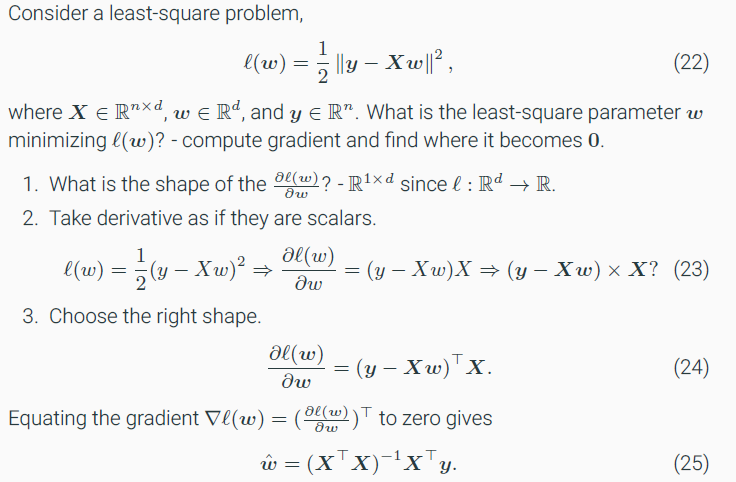
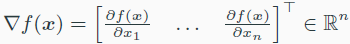(AI501) 5.linear algebra - vecter calculus
본 포스팅은 AI501 수업에서 제가 새로 알게 된 부분만 정리한 것입니다.
Derivates of $f:R^n → R$ (real-valued function)
- Partial derivate
$i = j이면 [e_i]_j = 1$
$i\neq j이면 [e_i]_j = 0$
- gradient
모든 coordinate에 대하여 partial derivate을 모아둔 것
Derivates of $f:R^n → R^m$ (vector-vector function)
Jacobian
f(x) 가 아래와 같을 때,
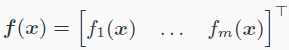
Jacobian matrix는 $m\times n$이다.
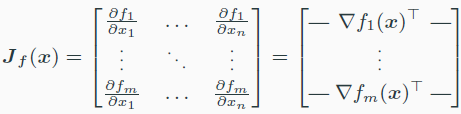
Total derivative
(totally) differentiable하다는 것은 Df(x)가 존재한다는 의미이다.
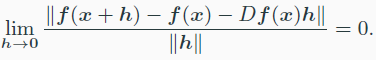
위 식에서 Df(x)는 (total) derivative라고 부른다.
D(f)는 x 주위에서 linear function을 잘 근사한다.
- $f:R^n → R^m$가 x에서 differentiable하다는 것은 모든 $\frac{\delta f_i}{\delta x_j}$가 존재하고, x에서 연속일 때이다. 이때 total derivates는 jacobian matrix와 같다.
- Euclidean space에서 f가 x에서 differentiable 하면, $\nabla f(x)^T=Df(x)$이다. 하지만 일반적으로 다르고, total derivate는 존재하는데, gradient는 존재하지 않는 경우도 있다.
Directional derivative
$f:R^n → R$ 일 때
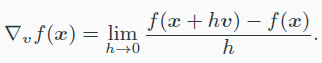
v 방향으로 directional derivate한 것이다.
또한 $f:R^n → R$ 이 differentiable하다는 것은 아래를 만족한다.
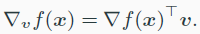
- $\nabla f(x)$는 가장 steepest 한 방향이다.
real-valued function $f:R^n → R$의 기본 규칙

Matrix-vector function $f:R^n → R^m$의 기본 규칙

예시로 f=Ax가 있을 때 $A \in R^{m\times n}, x\in R^n$이면
f(A)는 $R^{m\times n} → R^m$ 이므로
Df(A)는 $R^{m\times m\times n}$ 이다.
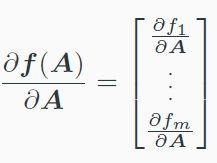
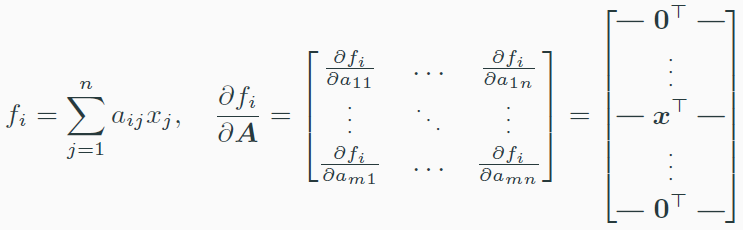
matrix-vector derivates는 아래와 같이 계산한다.
- derivates 결과의 shape를 추측
- scalar 처럼 계산
- shape를 맞춘다.
예시