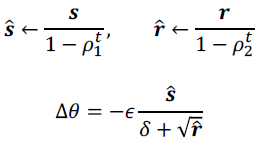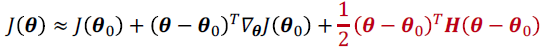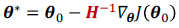(AI502) 6. optimization
본 포스팅은 AI502수업에서 제가 새로 알게 된 부분만 정리한 것입니다.
Convex Optimization problem
$f(\theta x + (1-\theta) y) \leq \theta f(x)+(1-\theta)f(y)$
- global optimum
- reliable & efficient algorithms
Taylor series Approximations
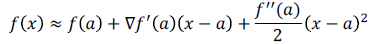
Surrogate Loss Function
- 0-1 loss 처럼 gradient 없는 함수의 proxy
minibatch 사용하는 SGD
- regularization effect
- multicore architecture에서 batch 크기가 작으면 제대로 활용x
Neural network optimization의 한계
- III-conditioning : critical point에 도달x
- Local minimum $\neq$ Global minimum
- Linear path experiments
- plateau, saddle point, flat regions
- gradient clipping
- long term dependecies
- vanishing
- exploding
learning rate
- convergence condition
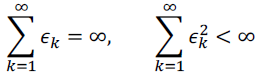
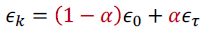
- $\epsilon_{\tau}$ 는 $0.01\times \epsilon_{o}$
- convex problem : $O(\frac{1}{\sqrt(k)})$
- strong convex problem : $O(\frac{1}{k})$
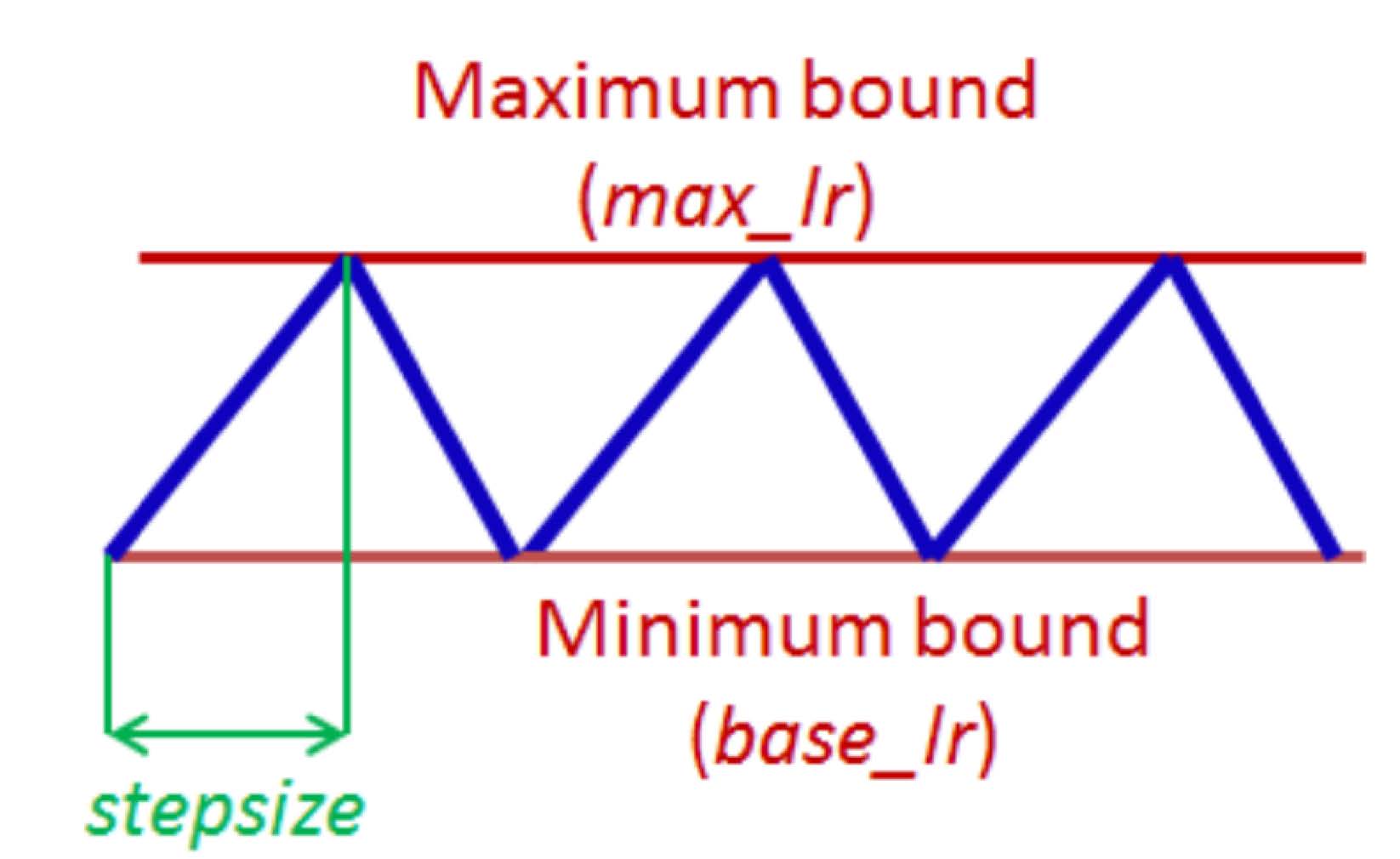
Cyclic Learning Rate
Momentum
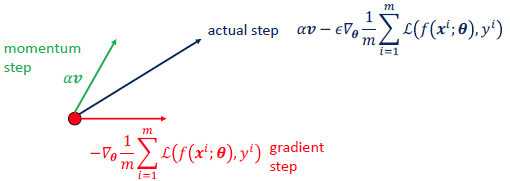
- $\alpha$가 크면 이전 gradient의 효과가 커진다.
- 2 문제 해결
- poor conditioning of hessian matrix
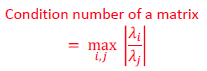
- condition number가 낮아지면, gradient descent를 잘 못한다. 한쪽방향으로의 derivative가 빠르게 증가하기 때문에
- 타원형
- variance in stochastic gradient
- poor conditioning of hessian matrix
Nesterov Momentum
- current velocity가 계산된 후에 gradient를 계산함.
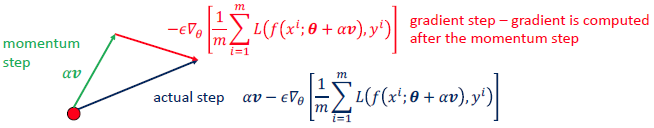
- strong convex problem : $O(\frac{1}{k^2})$
Initialization
- break symmetry
- large initial weights는 효과가 크다
- randomly하게 정해짐(Gaussian, uniform)
- random orthogonal matrices
- Adaptive Learning Rates : learning rate를 큰 것과 작은 것을 섞어서 사용
- AdaGrad : separate learning rate
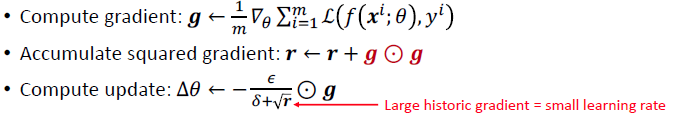
- gradient가 크면 learning rate가 크게 줄어듦
- gradient가 작으면 learning rate가 작게 줄어듦
- RMSProp
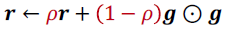
- 계속 줄어드는 것을 막음
- 이전 기록에서 얼마나 기억할지 $\rho$0
- Adam
- RMSProp + momenturm
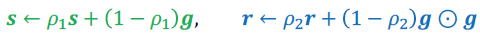
- bias correction
Approximate Second-Order Methods
- newton’s method
- damped newton
- Attacking Saddle Point Problem
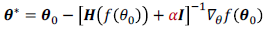
- $\alpha$가 크면 gradient descent랑 비슷해지고, 빠르게 수렴하는 장점이 사라진다.
- Saddle-Free Newton’s Method
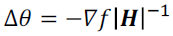
- ignore negative curvature
- Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno(BFGS)
- newton’s method 비슷하게 만든 것
- Hessian을 추정하기 위해서 최근 iteration의 curvature을 사용
- $H^{-1}$을 대신하여 M을 사용
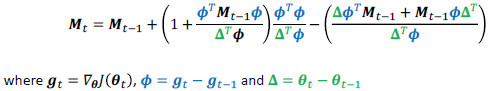
- $O(d^2) time, memory$
- Limited-Memory BFGS
- $M^{t-1}$을 identity matrix로 바꿔서 mamory cost를 크게 줄임.
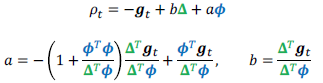
Optimization Strategies and Meta-Algorithms
- Coordinate Descent
- 한번에 1개의 variable만 optimize
- 여러 variable이 서로 연관되어 있으면 성능 안좋다.
- Polyak averaging
- parameter trajectory에 있는 여러 점을 평균
- convergence 보장
- non-convex일 때
- exponentially decaying average를 사용
- Supervised Pretraining
- simpler model을 학습하는 것
- step by step으로
- continuation methods
- smooth the objective
- curriculum learning
- 쉬운 것부터 어려운 것 학습